Getting a Mammogram
Mammography uses X-rays to create images of the breast. These images are called mammograms.
Learn more about mammograms.
Learn about findings on a mammogram.
Where to get a mammogram
Mammograms can be done in:
- Radiology centers and imaging centers
- Mammography clinics
- Hospital radiology departments
- Mobile vans
- Some doctors’ offices
To find a certified mammography center in your area, visit the FDA website.
What to expect
Preparing for a mammogram
Before the mammogram, you will undress from the waist up. So, it’s a good idea to wear a shirt you can remove easily.
Avoid using deodorants, antiperspirants, perfumes, powders or lotions on your breasts and underarm areas on the day of the exam. Ingredients in these products can show up on a mammogram and make it harder to read.
The mammogram procedure
Today, most mammography is done with digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT). DBT is also called “tomo” or 3-dimensional (3D) mammography. It takes multiple 2-dimensional (2D) digital images of the breast, and computer software combines the 2D images to create a 3D image.
During the exam, each breast is pressed between 2 plates and X-ray images are made. All the images are taken on the same machine, so you stay in one place while all the images are taken.
DBT may give a slightly higher radiation dose than 2D digital mammography (the main method in the past) [3,12]. This higher dose is within FDA guidelines though [3,12].
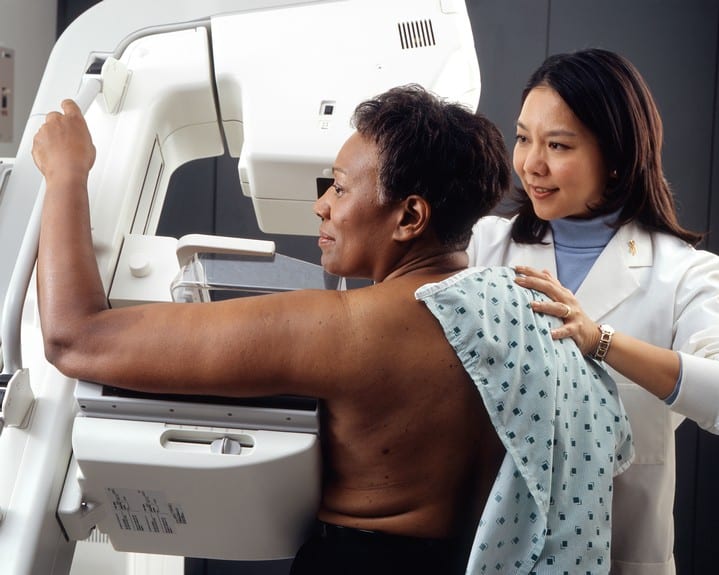
Discomfort and anxiety
The pressure during a mammogram may be uncomfortable, but it only lasts a few seconds. If you have concerns, talk with your health care provider about taking acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) before the exam. Your provider can also discuss other ways to help ease discomfort or anxiety during a mammogram.
On the day of the exam, let your technologist know if you have any concerns before they start or if you feel any discomfort during the exam.
How long does a mammogram take?
Getting a screening mammogram takes about 15 minutes from start to finish. Most of this time is positioning your breasts in the mammography machine.
When to expect results
Some centers give you the results of your mammogram at the time of your screening. With others, it may take up to 2 weeks to get your results.
If you don’t get your results within 2 weeks, contact your health care provider or the mammography center.
Don’t assume the results were normal because you didn’t get a report. Follow-up to get your results.
If you’re called back for more tests
In some cases, the mammogram wasn’t clear enough for the results to be read, and you will be called back for more tests. You will also be called back for more tests if a finding is abnormal.
Follow-up may include a diagnostic mammogram, breast ultrasound or breast MRI. In some cases, a breast biopsy may be needed.
It’s common to be called back for an abnormal finding on a mammogram. About 10% of women in the U.S. are called back for more tests after a screening mammogram [13-16].
It’s normal to be worried about an abnormal finding. However, in most cases, these findings are not breast cancer.
Sometimes, a mammogram shows an unclear or abnormal finding when in fact, there’s no cancer in the breast. This is called a false positive result. The chance of having a false positive result after 10 yearly mammograms is about 50% to 60% [4,17-18].
Watch our video of Komen Scholar Dr. Mariana Chavez MacGregor who talks about what to expect if you’re called back for more tests and why it’s important to get the needed follow-up tests.
Recall rates
The recall rate of a mammography center is the percent of women who are called back for follow-up tests. Some centers may share their recall rate with you. This information may help you understand your chances of being called back.
Learn about follow-up after an abnormal mammogram.
Click on the topics below to learn more.
Updated 03/17/25
This content is regularly reviewed by an expert panel including researchers, practicing clinicians and patient advocates.

